There’s another form of the Nobel Prize, called the Ig Nobel Prize. Don’t confuse this with the actual Nobel prizes. The Ig Nobels recognize scientific discoveries that “make people laugh, then think”.
‘The data on extreme human ageing is rotten from the inside out’ – Ig Nobel winner Saul Justin Newman – https://theconversation.com/the-data-on-extreme-human-ageing-is-rotten-from-the-inside-out-ig-nobel-winner-saul-justin-newman-239023
I started getting interested in this topic when I debunked a couple of papers in Nature and Science about extreme ageing in the 2010s. In general, the claims about how long people are living mostly don’t stack up. I’ve tracked down 80% of the people aged over 110 in the world (the other 20% are from countries you can’t meaningfully analyze). Of those, almost none have a birth certificate. In the US there are over 500 of these people; seven have a birth certificate. Even worse, only about 10% have a death certificate.
The epitome of this is blue zones, which are regions where people supposedly reach age 100 at a remarkable rate. For almost 20 years, they have been marketed to the public. They’re the subject of tons of scientific work, a popular Netflix documentary, tons of cookbooks about things like the Mediterranean diet, and so on.
Coffee prices are set to soar due to drought in this country
In Brazil, the world’s largest coffee producer, Almeida and other farmers have started grappling with the nation’s worst drought in more than seven decades and above-average temperatures. Almeida expected to harvest 120 sacks of coffee beans this harvest season, but instead managed just 100…At the same time, Vietnam, the world’s second-biggest coffee producer, is experiencing heat and drought, affecting its crops. Potential supply shortages in both countries have started driving up global coffee prices, according to the report.
“The patient requires coffee in the morning to function.” actual medical record entry from a case I worked on yesterday. Well, me too. My ability to function in the morning is going to cost more.
Does anyone remember Three Mile Island? I do. Looks like this nuclear plant may reopen.
Re-opened Three Mile Island will power AI data centers under new deal – https://arstechnica.com/ai/2024/09/re-opened-three-mile-island-will-power-ai-data-centers-under-new-deal/#p3
Pennsylvania’s Three Mile Island plant rose to infamy in 1979 when a partial meltdown in Unit 2 helped ignite panic over nuclear safety across the country. The new Microsoft deal would re-open the adjacent Unit 1, which was shuttered in 2019 “due to poor economics,” according to Constellation. If and when the plant reaches its planned 2028 re-opening, it would be among the first wave of shuttered nuclear plants being put back into service.
Yes, Microsoft! Might as well end this post with another Microsoft story.
Microsoft releases a new Windows app called Windows App for running Windows apps – https://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2024/09/microsoft-releases-a-new-windows-app-called-windows-app-for-running-windows-apps/
Have a nice weekend everyone!
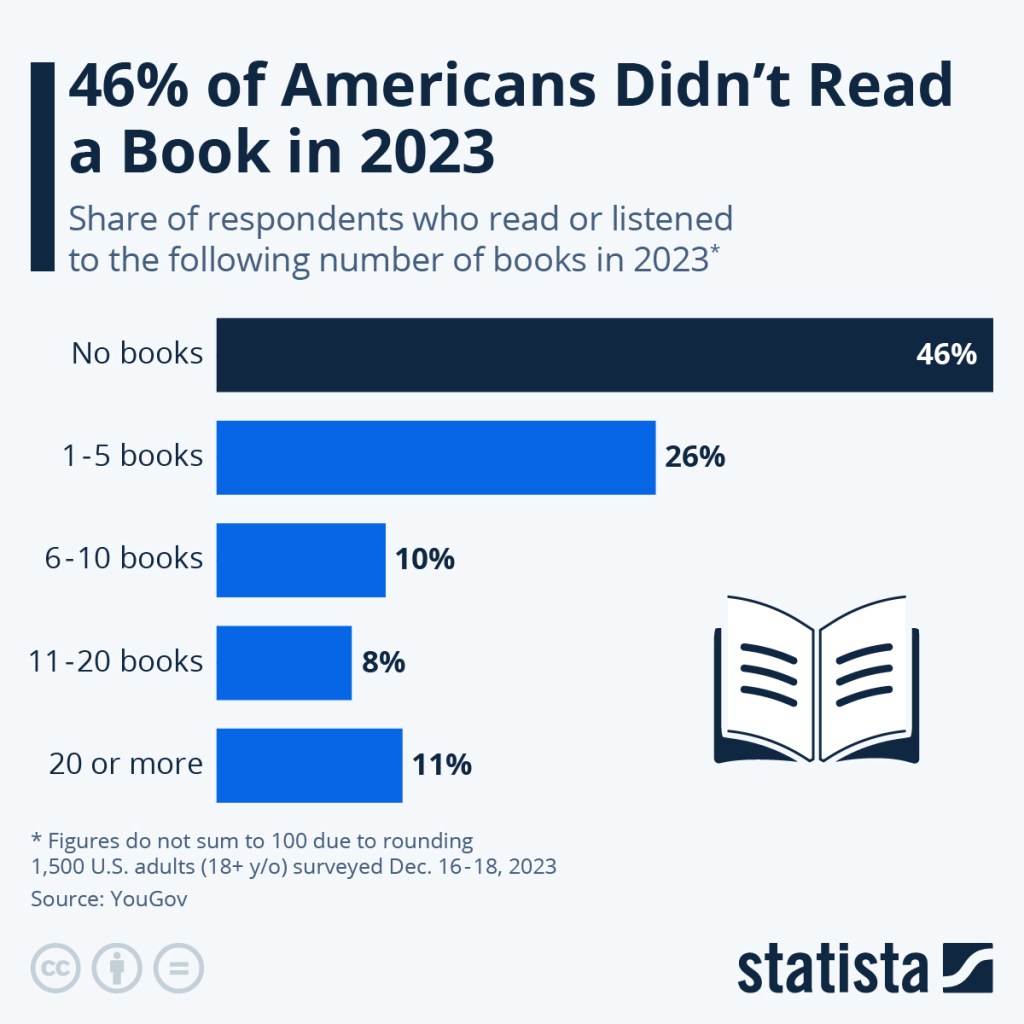
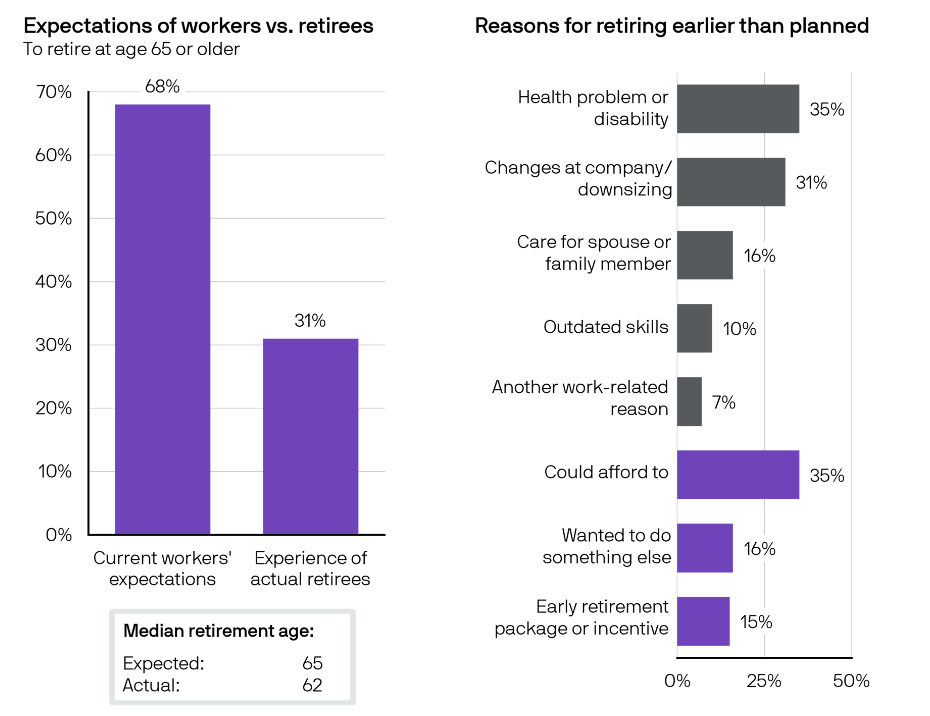


You must be logged in to post a comment.